In today’s digital era, the importance of cloud computing cannot be overstated. For IT professionals, the choice of cloud server provider is critical, impacting everything from operational efficiency to scalability and security. This article presents a comprehensive comparison of top cloud server providers, focusing on key features such as server options, uptime, scalability, security, pricing, user interface, customer support, and integration capabilities.
Toc
The Cloud Server Landscape

The cloud server market is rich and varied, offering solutions for businesses of all sizes and sectors. Whether you’re looking for shared, dedicated, or VPS hosting, the right provider can make a significant difference in your organization’s digital transformation. Key considerations include not just the technical specifications but also the reliability, cost-effectiveness, and customer service quality.
While evaluating the merits of various cloud server providers, it’s equally important to consider potential drawbacks that could affect your organization’s operations. One common issue is the complexity of pricing models, which can make cost predictions challenging and lead to unforeseen expenses. Additionally, limitations in customization and control over the server environment may hinder operations, particularly for businesses with specialized needs. Data sovereignty and privacy concerns also arise, as local laws affecting data storage and transfer can impact compliance. Furthermore, reliance on internet connectivity means that any disruptions in service can directly affect access to critical applications and data. Lastly, for businesses requiring high levels of technical support, the quality and responsiveness of customer service can vary significantly between providers, potentially affecting resolution times for technical issues. Keeping these factors in mind, let’s examine some of the top cloud server providers for IT professionals.
Cloud Server vs other kinds of traditional servers

High-Speed Connectivity and Uptime
A leading cloud server provider should guarantee an impressive uptime record, ideally aiming for 99.99% availability. This level of reliability ensures that services are consistently available to end-users without significant disruption. Factors contributing to strong network performance include state-of-the-art data center facilities, redundant network infrastructure, and advanced traffic routing technologies. These features help in mitigating the impact of hardware failures, natural disasters, and cyber attacks on service availability.
Overcoming Latency
Latency — the delay before a transfer of data begins following an instruction for its transfer — can significantly affect the user experience, particularly for real-time applications like video conferencing and online gaming. Providers that offer a wide distribution of data centers can help in minimizing latency by storing and processing data closer to the end-user. Additionally, using content delivery networks (CDNs) and direct connection options can further reduce lag, ensuring a smooth and responsive user experience.
Monitoring and Support
To uphold network performance and reliability, continuous monitoring and rapid support in case of issues are crucial. The best cloud server providers invest in comprehensive monitoring systems that alert IT staff to potential problems before they affect users. This proactive approach is complemented by 24/7 customer support from knowledgeable technicians, enabling swift resolution of any performance or reliability issues.
In conclusion, when evaluating cloud server providers, IT professionals must consider the intricacies of network performance and reliability. These factors are essential for maintaining the seamless operation of cloud services, impacting everything from user satisfaction to operational productivity.
Leading Cloud Server Providers
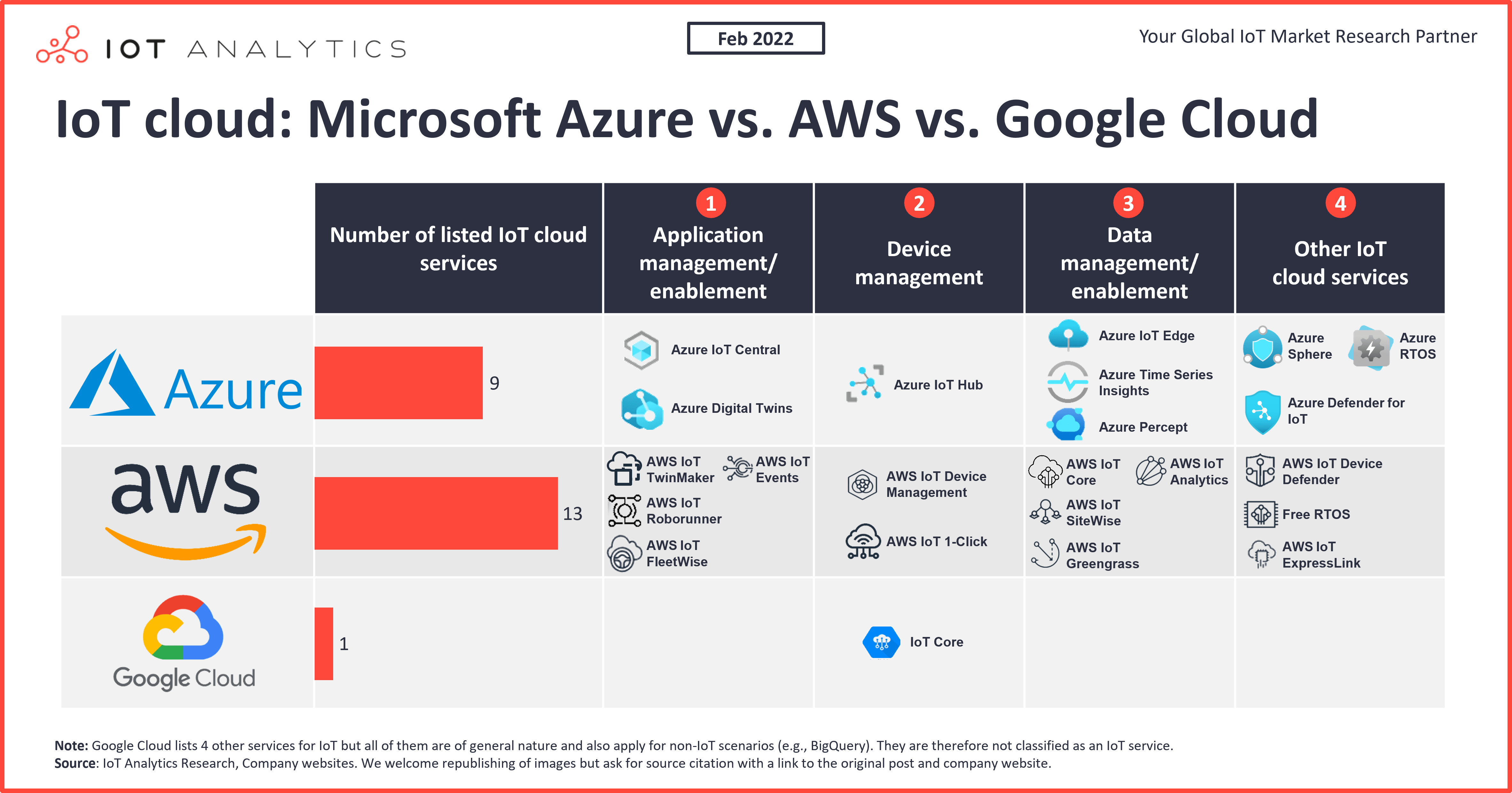
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Key Features:
- Range of Server Options: AWS offers an extensive array of compute instances, making it suitable for virtually any application.
- Uptime and Reliability: With a global network of data centers, AWS provides high availability and redundancy.
- Scalability: AWS’s auto-scaling feature allows businesses to adjust resources automatically according to demand.
- Security: AWS adheres to the highest security standards, with comprehensive compliance certifications.
- Pricing: Offers a pay-as-you-go model that helps businesses control costs effectively.
Case Study: A retail e-commerce company migrated to AWS, resulting in a 40% reduction in operational costs and a 50% boost in website performance.
Google Cloud
Key Features:
- Advanced Technologies: Google Cloud is renowned for its strength in AI and machine learning services.
- Scalability: Easily scales services with demand, ensuring that resources are available when needed.
- Security: Implements rigorous security protocols and complies with numerous industry standards.
- User-Friendly Interface: Provides a clean and intuitive management console.
- Integration: Offers seamless integration with various Google services and third-party applications.
Case Study: A healthcare startup used Google Cloud’s AI to develop a predictive analytics platform, showcasing its support for innovative projects.
Microsoft Azure
Key Features:
- Hybrid Capabilities: Azure excels in supporting hybrid cloud environments, allowing for flexibility in deployment.
- Security: Features comprehensive security tools and compliance with global and industry-specific standards.
- Scalability: Offers scalable services to accommodate growing business needs.
- Integration: Supports robust integration with Microsoft products and various third-party applications.
- Customer Support: Provides extensive support plans and a vast knowledge base.
Case Study: A financial services firm enhanced their infrastructure security and met compliance requirements using Azure.
Vultr
Key Features:
- Performance: Specializes in high-performance compute instances, ideal for demanding applications.
- Pricing: Competitive pricing models, offering a good balance between cost and performance.
- User Interface: Features a straightforward control panel for easy management.
- Global Reach: Operates a large network of data centers around the world, ensuring low latency.
- Customer Support: Offers 24/7 support through various channels.
Case Study: A gaming company improved user experience by leveraging Vultr’s compute resources for their online games.
IBM Cloud
Key Features:
- Hybrid Cloud: Strong focus on hybrid cloud solutions, supporting complex enterprise environments.
- Security: Robust security features and compliance with key industry regulations.
- Scalability: Easily scales resources to meet the demands of large-scale operations.
- Customer Support: Provides expert support and a comprehensive suite of services.
- Integration: Offers powerful integration capabilities with enterprise systems and third-party services.
Case Study: A multinational corporation adopted IBM Cloud for their hybrid strategy, enhancing their operational flexibility and integration.
Contrasting performance and reliability
When contrasting performance and reliability among cloud server providers, several factors come to the forefront. First, it’s important to consider the provider’s infrastructure, including the quality and geographical distribution of their data centers. Providers with modern, well-maintained facilities strategically located around the world can offer faster data retrieval times and improved resilience to physical disasters.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
AWS boasts an expansive and advanced network, renowned for its strength in performance and reliability. With a vast array of global data centers, AWS ensures low latency and high throughput for its users. Additionally, AWS’s commitment to innovation means they are constantly improving their services and infrastructure, which directly benefits performance metrics.
Microsoft Azure
Azure matches AWS in its global presence, offering a wide range of scalable services that cater to high-performance computing needs. Azure’s integration with Microsoft’s software ecosystem also provides a seamless experience for businesses already using Microsoft products and services. Its hybrid cloud capability ensures that organizations can maintain on-premises servers with the flexibility of the cloud, enhancing reliability.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
GCP differentiates itself with highly customizable computing solutions and a commitment to open source and multi-cloud environments. It is designed to offer high-speed and scalable networking features, ensuring efficient data movement. Its live migration of virtual machines minimizes downtime, thus providing uninterrupted service which is a critical reliability feature.
IBM Cloud
IBM Cloud offers a unique approach with its focus on AI and machine learning at the core of its cloud offerings, providing powerful analytics and performance capabilities. Its network is designed to support demanding workloads, offering both public and private cloud solutions to meet various needs on performance and data control, enhancing reliability for enterprise users.
In conclusion, while all these providers strive to offer the highest possible performance and reliability, differences in their infrastructure, technologies, and services cater to a diverse range of business needs and technical requirements. IT professionals must weigh each provider’s strengths against their organization’s specific demands to find the optimal cloud server solution.
Pricing and Cost Analysis
When evaluating cloud server providers, understanding the intricacies of their pricing models is crucial. Costs can vary significantly based on several factors, including resource consumption, data storage needs, network bandwidth requirements, and additional services like monitoring and automation tools. Here is a brief overview of how the major providers structure their pricing and key considerations for cost analysis.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
AWS operates on a pay-as-you-go pricing model, offering detailed customization of resources which allows businesses to pay only for what they use. However, navigating the complexity of AWS’s pricing can be challenging, as costs can fluctuate based on specific services, data transfer rates, and optional features like enhanced support. AWS offers cost management tools to aid in tracking and optimizing spending.
Microsoft Azure
Azure provides a flexible pricing strategy similar to AWS, with pay-as-you-go rates for over 600 services. It encourages savings through reserved instances and hybrid benefits for customers using Microsoft software. Azure’s pricing calculator helps businesses estimate costs before committing, and its approach to enterprise agreements can offer significant discounts to large organizations.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
GCP aims to be competitive by offering a simple and transparent pricing model. It includes sustained-use discounts, which automatically lower prices for virtual machines used regularly throughout the month. Additionally, GCP’s custom and pre-defined machine types allow for fine-tuned control over resources, helping to reduce costs without sacrificing performance.
IBM Cloud
IBM Cloud’s pricing varies, offering both subscription-based plans and pay-as-you-use options for flexibility. It distinguishes itself with its commitment to enterprise clients, offering tailored packages which can include both cloud and hybrid environments. IBM Cloud also provides a cost estimator tool and often negotiates pricing based on the client’s specific needs and scale of use.
Cost Analysis Considerations
Comparing cloud provider costs involves more than just looking at the price of individual services. Businesses need to consider the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes direct and indirect costs such as operations, bandwidth, and support. Identifying and forecasting usage patterns can also help in choosing committed use or reserved instances that offer cost savings. Lastly, leveraging cost management and optimization tools provided by these platforms can lead to more efficient resource use and reduced expenses.
Choosing the right cloud server provider for your business
The impact of choosing the right cloud server provider on businesses
The impact of choosing the right cloud server provider on businesses is profound and multifaceted. With the appropriate cloud infrastructure in place, companies can achieve unparalleled scalability, allowing them to easily adjust their resources up or down based on current demand. This flexibility is crucial for businesses aiming for growth or those that experience seasonal fluctuations in their operations.
In addition to scalability, the security features offered by top cloud server providers are essential for protecting sensitive data. Advanced encryption, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems can significantly mitigate the risk of cybersecurity breaches, which is particularly important in an era where data breaches can have devastating consequences for businesses’ reputations and finances.
Furthermore, the operational efficiency that cloud servers bring cannot be understated. By offloading hardware maintenance and upgrades to the provider, businesses can concentrate on their core operations, fostering innovation and improving service delivery. The use of cloud servers also promotes collaboration among team members by facilitating easy access to shared documents and applications from any location.
Real-life Use Cases of Cloud Servers
The application of cloud servers spans across various industries, proving to be a versatile solution for many organizational needs. Here are some real-life use cases that highlight the practical benefits of leveraging cloud computing.
E-commerce Scalability
For e-commerce platforms, managing the fluctuating demand, especially during peak shopping seasons or sales events, is crucial. Using cloud servers, these websites can dynamically scale their resources to handle spikes in traffic, ensuring smooth user experiences and minimizing lost sales due to website downtime. An excellent example is how major online retailers scale their operations during Black Friday or Cyber Monday sales, accommodating millions of simultaneous shoppers.
Disaster Recovery and Data Backup
Businesses across sectors use cloud servers for disaster recovery (DR) and data backup solutions. By storing critical data off-site in a secure cloud environment, companies can protect against data loss due to natural disasters, cyber-attacks, or system failures. The ability to quickly recover data and restore operational functionality minimizes downtime and the associated costs. This use case is particularly relevant for financial institutions and healthcare organizations, where data integrity is paramount.
Remote Work and Collaboration
The shift towards remote work has been facilitated by cloud computing, allowing employees to access work files and applications from anywhere, at any time. Cloud servers provide the backbone for collaboration tools and virtual desktop infrastructures (VDIs) that support telecommuting. Businesses in technology, education, and professional services sectors have leveraged these capabilities to maintain productivity while also offering flexibility to their workforce.
Development and Testing Environments
Cloud servers offer a cost-effective and scalable solution for creating development and testing environments. Companies developing software can spin up instances as needed to test new applications or updates without investing in physical hardware. This flexibility accelerates development cycles and enables agile methodologies by allowing developers to quickly deploy, test, and iterate on their projects. Startups and large tech companies alike have benefited from these capabilities, reducing time to market for new software solutions.
Big Data Analysis and Machine Learning
Organizations leverage cloud servers to process and analyze large datasets, utilizing the computational power and scalability of the cloud for big data analytics and machine learning projects. Industries such as retail, finance, and telecommunications use these insights to drive decision-making, personalize customer experiences, and innovate product offerings. For example, streaming services analyze viewer data to recommend personalized content, enhancing user engagement and satisfaction.
By showcasing these diverse use cases, it becomes clear that cloud servers are not just about providing IT infrastructure but are a strategic asset that can drive operational efficiency, innovation, and competitive advantage across various business domains.
Conclusion
Choosing the right cloud server provider is a pivotal decision for IT professionals. By focusing on the specific needs of your business and considering factors like scalability, security, and pricing, you can select a provider that not only meets your current requirements but also supports your future growth. Whether it’s AWS’s extensive service offerings, Google Cloud’s advanced technologies, Azure’s hybrid capabilities, Vultr’s performance focus, or IBM Cloud’s enterprise solutions, each provider has unique strengths. By leveraging these platforms, businesses can achieve greater efficiency, innovation, and competitive advantage in the digital landscape.